MENISCUS TEAR
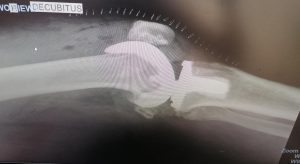
The knee can present multiple problems to patients. The most common of these has to be a tear of the meniscus. A meniscus is a horseshoe shaped disc found in the weightbearing compartment of the knee. Each knee has two. The meniscus is typically torn during a twisting motion of the knee with the foot fixed. Symptoms include pain, swelling and clicking.
Treatment usually consists of an arthroscopy with removal of the torn portion. If it is torn in a certain way, the meniscus can also be repaired.
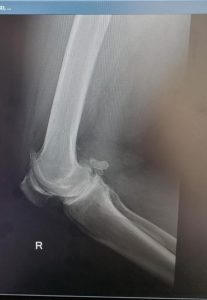
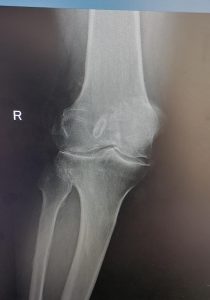
Recovery is short and risks associated are low. See the torn meniscus and the removed tear below.
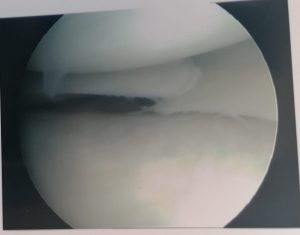
TORN MENISCUS 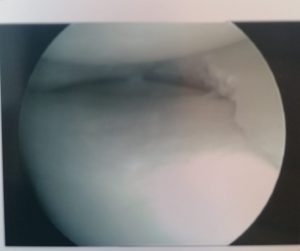
REMOVED TEAR
KNEE REPLACEMENT
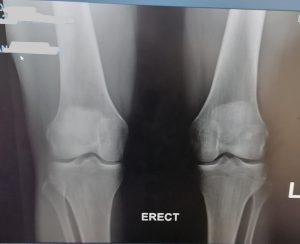
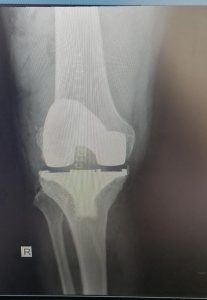
As the knee ages it may come to a point where cartilage has eroded away to expose bone. Bone grinding on bone as a person is walking is very painful. Fortunately orthopaedic science has evolved to a solution whereby the knee can be replaced with a mechanical prosthesis.
Presently, the results are generally very good with excellent pain relief and mobility after the operation. Longevity of the prosthesis has improved to a point where the 10 year survival is more than 95% in some series.
As all surgery, the procedure is not entirely risk free. Deep venous thrombosis at 1% incidence and infection at 0.4% are most common complications, but stiffness, bleeding, nerve injury etc. can occur.
Below see the pre operative pictures of a normal knee, a diseased knee and a replaced knee.
HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY
Some patients have degeneration of one compartment of the knee, but they are too young to have a total knee replacement. For them it makes sense to change the alignment of the leg so the weightbearing axis runs through the healthy compartment. This allows pain free mobilization for several years. A knee replacement can then be done when the patient is older.
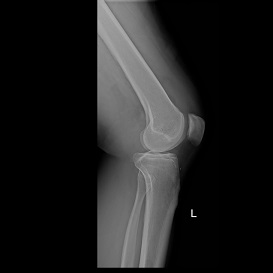
BEFORE OPERATION 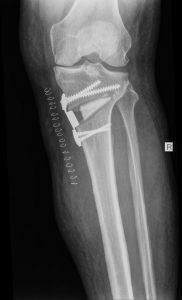
AFTER OPERATION